Labs
Overview
Labs is a open-source project that provides a platform for learning Application Security in a practical way. It offers a variety of hands-on ephemeral labs and exercises that cover different aspects of application security.
Features
- Hands-on Labs: Interactive labs that allow you to practice your skills in a safe environment.
- Ephemeral Environments: Each lab runs in its own isolated environment, ensuring that your work does not affect others and can be reset easily.
- Evaluators: Automated tools that assess your work and provide feedback, helping you learn and improve.
- Manual Review: In addition to automated evaluations, some labs may require manual review by instructors or peers for more complex tasks.
Stack
The Labs project is built using a stack that includes:
- Frontend: Angular (with PrimeNG).
- Backend: Golang (with Echo).
- API: Golang (with Echo).
- Orchestrator: Kubernetes for managing lab environments.
- Database: PostgreSQL, Redis and MongoDB.
Architecture
The Labs project is designed to be modular and extensible, allowing for easy addition of new labs and exercises. The architecture includes:
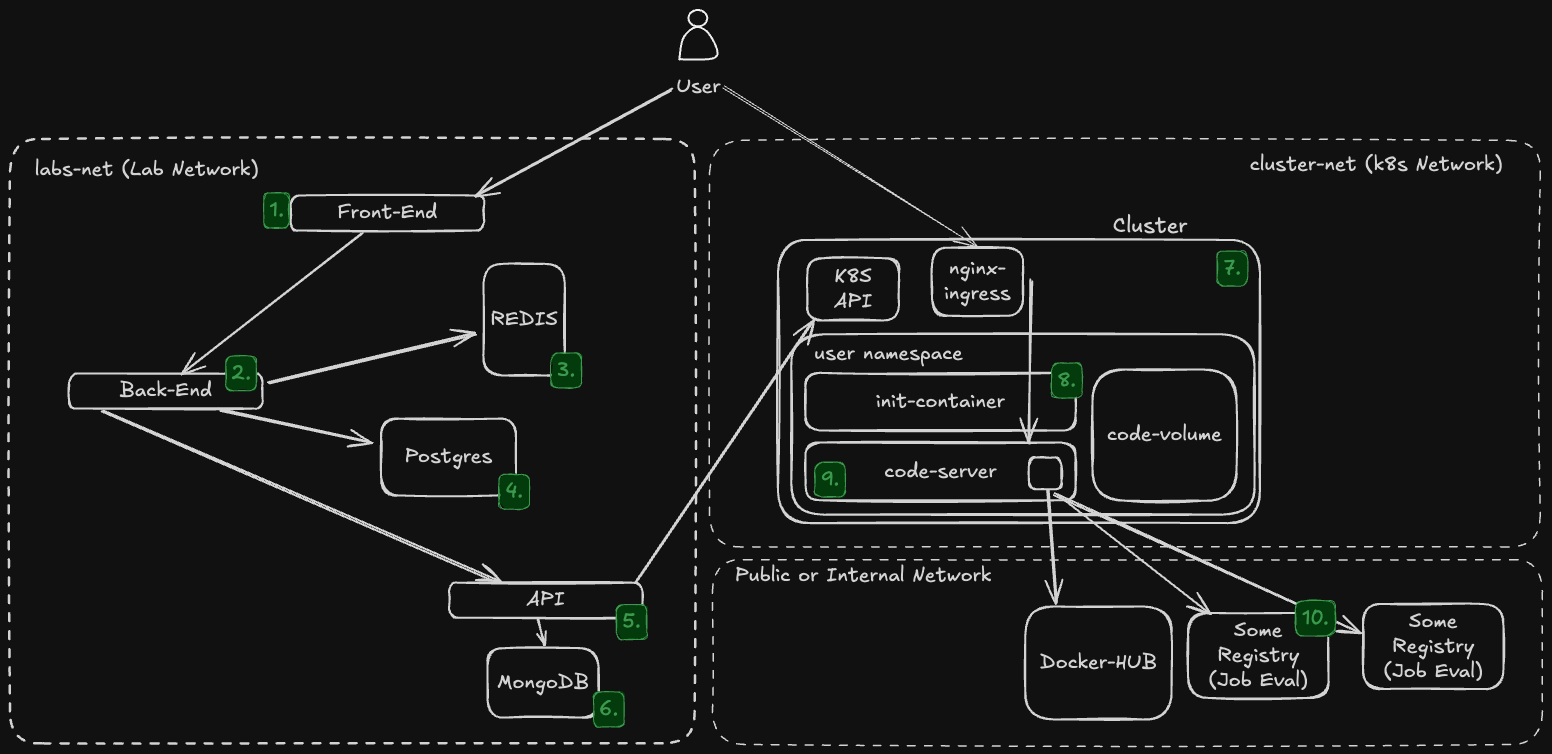
- Frontend: A user-friendly interface, providing access to labs and exercises.
- Backend: A server that plays the role of BFF (Backend for Frontend): handling requests from the frontend, performing business logic, managing user labs sessions, and communicating with the API (Cluster-API) and database.
- REDIS: A redis instance used as a caching layer to store session data (lab session attempts) and improve performance.
- Postgres: A database that stores user progress, lab configurations and evaluation results.
- API: An API (Cluster API) that manages the lifecycle of lab environments, interacting with Kubernetes: including creation, deletion, and status updates.
- MongoDB: A database used for storing additional data related to labs and exercises, such as configurations and metadata.
- Kubernetes: The orchestrator that manages the deployment and scaling of lab environments, ensuring they are ephemeral and isolated.
- Init Containers: Special containers that run before the main application containers in a pod, used for setup tasks, such as loading lab code or configurations.
- Code Server: A service (container) that provides a web-based code editor for users to write and test their code within the lab environments. It's based on a opensource project. More details about Code Server can be found here: https://github.com/coder/code-server
- Evaluators Jobs: Jobs that run evaluations on user lab submissions. It allows for automated assessment of user submissions, providing immediate feedback and grading. Examples of evaluators include:
- Static Code Analysis: Analyzes the user code for security vulnerabilities without executing it.
- Exploitability Analysis: Evaluates the exploitability of vulnerabilities in the code that the user submitted.
Navigation
🗃️ 🚀 Getting Started
2 items
🗃️ Guides and Tutorials
4 items
📄️ Roadmap
Here are some of the key features and improvements we plan to implement in the near future: